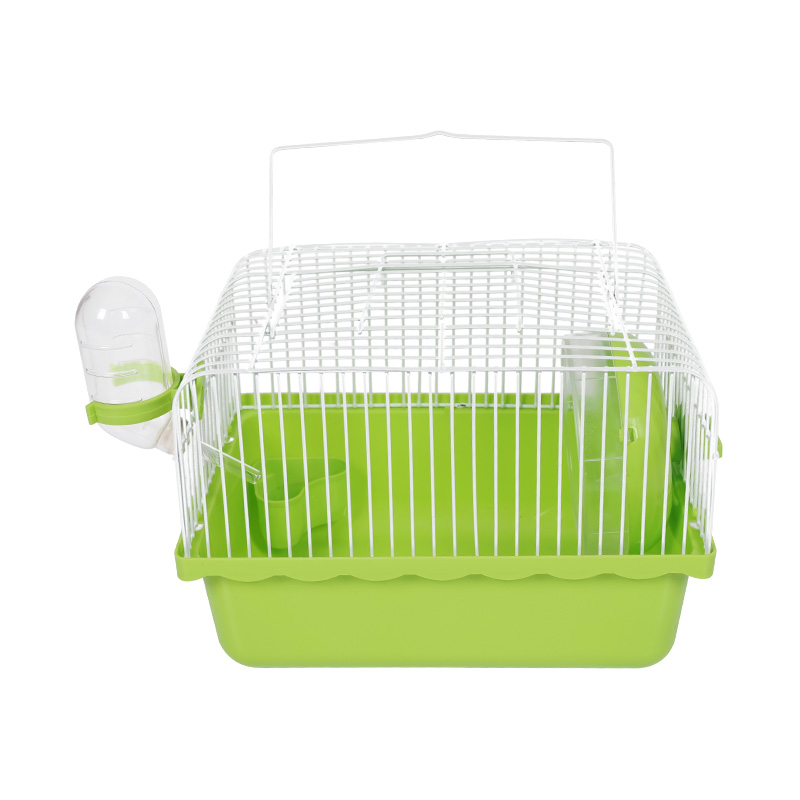
Preventing pets from getting hurt or damaging Pet Cages is an important measure to ensure pet safety and extend the life of the cage. The following analyzes how to effectively prevent these problems from multiple angles and provides specific solutions:
Prevent pet injuries
Choose safe materials and designs
Smooth surface:
Make sure the welding points, seams and edges of the cage are smooth to avoid sharp edges or protruding parts scratching pets.
For metal cages, you can choose polished products; for plastic cages, make sure there are no burrs or cracks.
Non-toxic materials:
Use non-toxic and environmentally friendly materials to prevent pets from ingesting harmful substances after chewing.
If using wood or fabric cages, make sure the surface coating or dye is harmless to pets.
Reasonable size and layout
Sufficient space for activities:
Pets should be able to stand, turn around and lie down freely in the cage to avoid bumps or discomfort caused by small space.
For small pets (such as hamsters or rabbits), layered designs can be added to increase the range of activities.
Soft mats: Lay soft mats or mattresses on the bottom of the cage to prevent your pet from coming into direct contact with hard surfaces, reducing joint stress and the risk of abrasions.
Avoid pinching
Strong latches and door design: Make sure the latch design of the cage door is simple but strong to prevent your pet from accidentally opening it or pinching its paws.
Check that the hinges of the cage door are smooth to avoid pinching your pet's nose or paws.
Reasonable vent size: The design of the vents should avoid the risk of your pet's head or paws getting stuck, especially for small pets.
Prevent your pet from destroying the cage
Choose the right material based on your pet's behavior
Bite-resistant material: For pets who like to chew (such as rodents or puppies), choose a strong and durable material such as high-density plastic or metal.
Avoid using fabrics or low-quality plastics that are easily damaged by chewing.
Reinforced design: For large dogs or other strong pets, choose a thickened metal cage or a design with reinforcing ribs.
Additional reinforcement can be done at key parts of the cage (such as the door frame or joints).
Provide alternative distractions

Toys and chews:
Place chew-resistant toys or special chews in the cage to meet the pet's chewing needs and reduce damage to the cage.
Provide chew sticks or wooden toys for rodent pets.
Regular interaction:
Increase the interaction time with the pet to prevent the pet from chewing the cage due to boredom.
Adjust the pet's behavioral habits
Training and guidance:
Through positive reinforcement training (such as reward snacks or praise), let the pet gradually adapt to the cage environment and reduce destructive behavior.
If the pet has the habit of chewing the cage, it can be stopped by spraying bitters (non-toxic spray that pets hate).
Daily maintenance and inspection
Regularly check the integrity of the cage
Structural inspection:
Regularly check the welding points, locks and joints of the cage for looseness, rust or damage.
If cracks or deformation are found, repair or replace the cage in time.
Cleaning and disinfection:
Clean the cage regularly to prevent dirt accumulation that may cause pets to eat or get infected.
Use pet-specific disinfectants to clean the cage and avoid using harsh chemicals.
Replace worn parts
Trays and mats:
If the tray or mat at the bottom of the cage is damaged or aged, it should be replaced in time to prevent the pet from getting hurt or swallowing fragments.
Locks and doors:
If the lock of the cage door is loose or damaged, it may cause the pet to escape or get pinched, and it needs to be repaired or replaced immediately.
Preventing pets from getting hurt or damaging pet cages requires multiple aspects such as material selection, design optimization, daily maintenance, and behavior management. By choosing a safe and durable cage, providing a comfortable environment, regular inspections and maintenance, and guiding the pet's behavioral habits, the risk of pets getting hurt or damaging the cage can be effectively reduced. At the same time, it is also very important to take personalized protective measures for pets in special scenarios or with special needs.


 English
English Español
Español